Public Opinion Analysis
In May 2024, the Dor Moriah Analytics Center and the Geocartography Sociological Center conducted a comprehensive sociological survey on the outcome of Vladimir Putin’s Russian presidential election. The election concluded with Putin’s victory. While the United States and European Union initially indicated they would not recognize election results in certain regions, the U.S. leadership officially acknowledged the election outcome on May 7-9. Representatives from several EU countries and Israel attended the Russian president’s inauguration ceremony.
Meanwhile, Global South nations, including Persian Gulf states, India, China, Turkey, South Africa, Brazil, and others, immediately congratulated Vladimir Putin on his victory.
To examine Israeli attitudes toward the Russian presidential election and its impact on the confrontation between the Collective West and the Global South, 1,006 Israelis were surveyed. The study was conducted through a special internet survey of respondents aged 18 and older who comprise a national representative sample of Israel’s population (with Jewish and Arab sectors selected as part of this population).
Recognition of Russian Elections: Multi-Factor Analysis
The study revealed a complex picture of society’s attitudes toward global political processes. The survey, conducted among both Jewish and Arab sectors, showed significant differences in views between religious and secular citizens, as well as among supporters of various political movements.
The Israeli public’s reaction to the U.S. and Western countries’ recognition of Russia’s presidential election results demonstrates an interesting correlation between religious beliefs and political views.
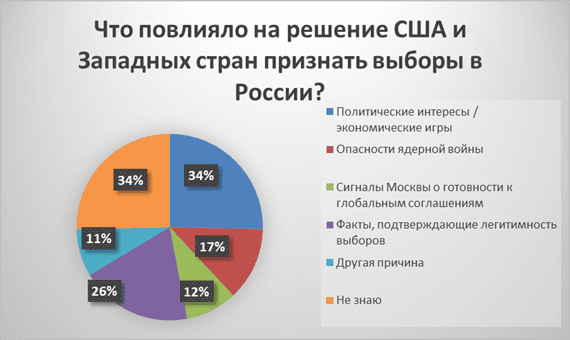
Political Interests as a Key Factor
The most popular explanation (about one-third of respondents) relates to political and economic interests. A clear correlation emerges:
– Among right-wing political forces, 49.1% of respondents support this view
– Among centrists, the figure stands at 40.4%
– The left shows more moderate support for this version – 32.8%
Religious Factor in Legitimacy Assessment
The distribution of opinions regarding election legitimacy presents particular interest:
– Religious Jews and Haredim more frequently (32.1%) consider the presence of legitimacy-confirming facts as the decisive factor
– Secular Israelis demonstrate a more skeptical attitude – only 25.7% share this view
– Notably, among right-wing political forces, support for this version reaches 41.2%
Global Confrontation: Analysis of Predictions
Religious Aspect in Consequence Assessment
The study revealed substantial differences in evaluating the impact of Russian elections on global confrontation:
– 43.4% of religious Jews and Haredim expect intensified confrontation
– Only 22.8% of tradition-observing Jews share this opinion
– Secular Israelis occupy an intermediate position – 39.1%
Political Spectrum and Forecasts
Analysis across the political spectrum shows an even more interesting picture:
– Centrists demonstrate the highest concern (50.9% expect intensified confrontation)
– Right and left wings show moderate pessimism (39.2% and 45.6% respectively)
– Notably, among “other” political groups, only 16.8% expect intensified confrontation
Palestinian-Israeli Conflict in the Context of Global Changes
Impact of Global South’s Strengthening
The data shows an unexpected correlation between religiosity and optimism regarding conflict resolution:
– 34.7% of religious Jews and Haredim believe that strengthening the Global South will accelerate conflict resolution
– Secular Israelis are more reserved in their assessments – 27.8%
– Meanwhile, 31.3% of secular respondents expect the settlement process to slow down
Political Spectrum and Prospect Assessment
Political views significantly influence the assessment of settlement prospects:
– Right-wing forces show the highest optimism (38.2% expect accelerated settlement)
– The left demonstrates greater skepticism – only 25.8% share the optimistic forecast
– Moderate left more often than others are uncertain (35%)
Israel’s Geopolitical Choice: Detailed Preference Analysis
Religious Factor in Orientation Choice
The study revealed clear differences in geopolitical preferences based on religiosity:
Secular Israelis demonstrate the following opinion distribution:
– 35.2% favor orientation toward the Collective West
– 24.3% support neutrality
– 29.8% prefer orientation toward the Global South
Meanwhile, religious Jews and Haredim show different priorities:
– 22.4% support Western orientation
– 35.7% favor neutrality
– 19.6% lean toward Global South orientation
Political Affiliation and Foreign Policy Preferences
Analysis across the political spectrum shows a complex picture:
– Right-wing forces demonstrate the strongest support for pro-Western orientation (36.3%)
– The left more often advocates for neutrality (36%)
– Support for Global South orientation is relatively uniform across the political spectrum (21-28%)
Conclusion
The detailed analysis reveals a complex mosaic of opinions and preferences in Israeli society. Religious factors and political beliefs play a key role in shaping views on global processes and Israel’s place in the changing world. The absence of clear consensus on key issues reflects an ongoing process of searching for an optimal development path for the country amid the transformation of the global order.
